For years, decentralized applications (dApps) have operated within the confines of general-purpose blockchains, accepting network-level transaction ordering and fee structures as immutable realities. Yet, as the value generated by dApps grows and the market matures, a new paradigm is emerging: Application Controlled Execution (ACE). This approach is rapidly redefining how custom app-chains can shape their own specialized fee markets, unlocking new layers of efficiency, sovereignty, and economic alignment.

The Shifting Landscape: From Shared Layer 1s to Application Sovereignty
Traditional blockchains like Ethereum prioritize neutrality and security but often at the cost of flexibility. Every transaction competes for blockspace in a global fee auction, leading to unpredictable costs and limited ability for dApps to innovate with their own market mechanisms. As highlighted in recent research (Modular Blockchains and the Rise of the App Chain Era), teams are increasingly seeking alternatives that allow them to tailor execution environments for their specific needs, especially when it comes to fee markets.
This shift is not just theoretical. According to Dapp.Expert, Solana’s roadmap includes a move toward ACE by 2027, aiming to revolutionize transaction mechanics and empower applications with control over execution sequencing. The goal? Enable dApps to experiment with new microstructures such as in-block auctions or custom prioritization rules, capabilities simply not possible on shared Layer 1s.
What Is Application Controlled Execution (ACE)?
Application Controlled Execution gives dApps unprecedented authority over transaction sequencing, inclusion criteria, and even how fees are distributed. Rather than ceding these decisions to protocol-level validators or miners, applications can:
- Define custom rules for transaction ordering, such as prioritizing certain user groups or use cases
- Auction blockspace internally, capturing Maximum Extractable Value (MEV) for their own ecosystem rather than leaking it externally
- Create specialized fee markets, including zero-fee models, loyalty-based pricing tiers, or real-time auctions tailored to application logic
This model aligns incentives more closely with users and developers while providing a laboratory for innovation in blockchain economic design.
The Economic Imperative: Why Specialized Fee Markets Matter Now
The current market context underscores why ACE is so timely. Despite being engines of user activity and revenue generation, most applications still trade at massive discounts compared to infrastructure protocols, on average at ~300x lower revenue multiples, according to Syncracy Capital’s latest analysis. The reason? Infrastructure captures value through native tokens and protocol fees while applications remain tethered to fixed fee models set by underlying chains.
With ACE-powered app-chains, this dynamic changes fundamentally. By capturing MEV internally and designing bespoke fee structures that reward loyal users or subsidize high-value transactions, dApps can finally realize business models that reflect their true value creation potential. This is not only an economic opportunity but also a catalyst for deeper user engagement and network effects.
Key Benefits of Specialized Fee Markets in ACE App-Chains
-

Enhanced Economic Sovereignty: ACE enables applications to capture and redistribute Maximum Extractable Value (MEV) within their own ecosystem, increasing revenue potential for dApps and their communities.
-
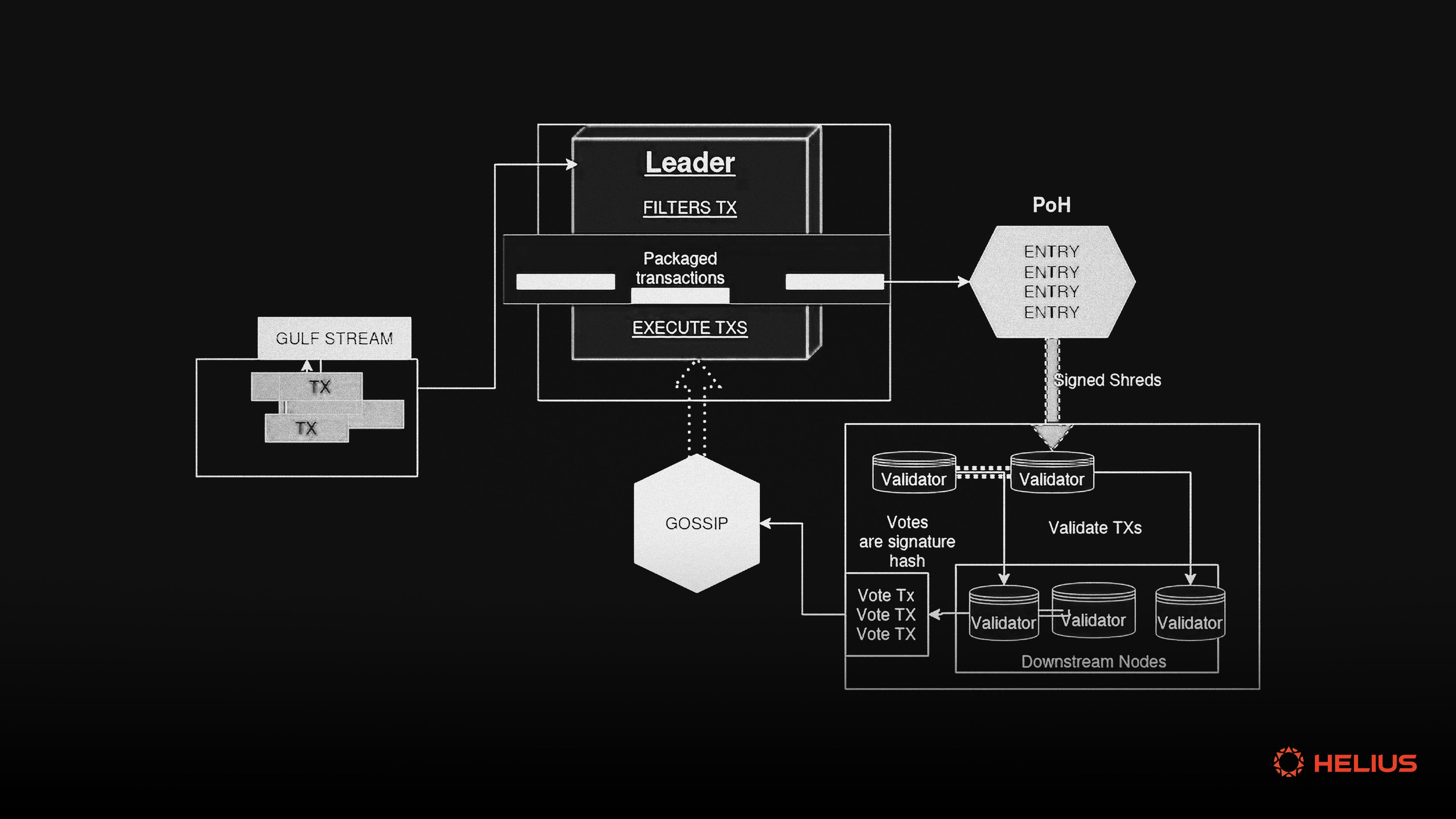
Customizable Transaction Prioritization: With specialized fee markets, applications can define custom rules for transaction inclusion and ordering, optimizing user experience and enabling advanced features like in-block auctions or priority fee sorting, as seen in Solana’s ACE roadmap.
-
Improved Efficiency and Lower Costs: By tailoring fee markets to specific application needs, app-chains can reduce congestion and lower transaction costs compared to general-purpose blockchains, delivering a smoother experience for end-users.
-

Innovation in Market Microstructure: ACE app-chains empower teams to experiment with new fee models and execution logic, such as cancel prioritization or in-block auctions, fostering rapid innovation and differentiation (referenced in The Internet Capital Markets Roadmap).
-
Alignment with Modular Blockchain Trends: Specialized fee markets fit seamlessly with the modular blockchain paradigm, allowing app-chains to focus on application-specific optimization while leveraging shared infrastructure for security and scalability (as discussed by Orbis86 and Supra).
A Glimpse into the Future: Solana’s Internet Capital Markets Roadmap
The movement toward application-specific blockchains is gaining momentum across ecosystems. Solana’s recently unveiled Internet Capital Markets Roadmap exemplifies this trend by proposing a world where transactions are sorted by priority fees at the application level, not dictated solely by protocol-layer auctions (source). This enables sophisticated execution logic such as cancel prioritization or in-block batch auctions, features tailored for modern DeFi protocols and beyond.
The promise of ACE extends far beyond DeFi; NFT marketplaces could implement royalty-preserving order books while gaming chains might offer free transactions during peak events. By putting execution control back into application hands, we’re witnessing the dawn of truly programmable blockchain economics, where efficiency meets creativity without compromise.
What sets ACE apart is its ability to transform the relationship between dApps and their users. Instead of being passive fee payers, users become active participants in a dynamic market designed around their needs. For example, a decentralized exchange could introduce real-time auctions for blockspace, allowing traders to bid for execution priority based on market volatility. Loyalty programs may reward long-term users with discounted or even zero-fee transactions, while high-frequency traders could pay a premium for guaranteed inclusion. This flexibility is simply unattainable on monolithic Layer 1 chains.
The technical underpinnings of ACE are equally compelling. By giving applications fine-grained control over transaction sequencing, app-chains can experiment with mechanisms like batch settlements, in-block order matching, or time-weighted fee curves. This not only optimizes for throughput and latency but also minimizes value leakage to external actors, a persistent challenge in traditional blockchains where MEV extraction often benefits validators at the expense of end-users.
Practical Examples: Custom Fee Structures in Action
Let’s look at how specialized fee markets are already reshaping user experience and business models:
Real-World Examples of Custom Fee Structures Enabled by ACE
-

Solana’s Priority Fee Markets: Solana enables applications to set priority fees for transaction inclusion, allowing dApps to experiment with custom execution logic such as in-block auctions and cancel prioritization. This flexibility is part of Solana’s roadmap to modernize market microstructure using ACE by 2027.
-
Eclipse’s Local Fee Markets: Built on the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM), Eclipse leverages ACE to implement local fee markets, letting each application define its own pricing model for transactions. This approach optimizes fee structures for specific app needs and user experiences.
-
Osmosis Custom AMM Fees: As a leading app-chain in the Cosmos ecosystem, Osmosis allows liquidity pools to set custom swap fees and even experiment with dynamic fee models, made possible by application-level control over transaction execution and fee logic.
-

dYdX v4 App-Chain Fee Model: The dYdX v4 app-chain, built on Cosmos SDK, implements a custom trading fee structure that rewards validators and stakers based on trading activity, rather than generic blockspace usage, demonstrating application-specific fee market design.
-

Injective Protocol’s Auction-Based Fees: Injective Protocol uses on-chain auctions for block proposer selection and fee collection, allowing the protocol to capture and redistribute MEV within its ecosystem, a direct result of application-controlled execution.
From NFT platforms implementing creator-first royalty splits to enterprise chains enforcing compliance-driven fee schedules, the spectrum of possibilities is vast. Even within DeFi, protocols are piloting in-block auctions for liquidation priority and offering gas rebates to liquidity providers, innovations made possible by application-level execution control.
Challenges and Design Considerations: Building Sustainable App-Chains
Of course, greater flexibility comes with new responsibilities. Designing fair and efficient custom rollups requires careful thought around incentive alignment, security assumptions, and user transparency. Poorly designed fee markets can lead to fragmentation or unintended forms of value extraction if not monitored closely.
Developers must also consider interoperability: as more app-chains adopt ACE, cross-chain composability becomes both an opportunity and a challenge. How will liquidity flow between chains with radically different fee structures? What standards will emerge for MEV redistribution across interoperable rollups?
Key Takeaways for Builders
- User-centric economics: Design fee markets that reflect your application’s unique value drivers.
- Experimentation is vital: Use ACE as a laboratory for new execution logic, pilot small changes before scaling up.
- Transparency builds trust: Clearly communicate fee models and sequencing logic to your community.
- Monitor MEV flows: Implement robust analytics to ensure value accrues where intended.
The rise of Application Controlled Execution marks a turning point for blockchain scalability and economic design. By empowering dApps to tailor their own specialized fee markets, ACE unlocks sustainable growth models that reward innovation and align incentives across stakeholders. As Solana, Eclipse, and others push this frontier forward (Dapp.Expert), the next era of custom app-chains will be defined by flexibility, not just in code but in economics itself.






