Application-specific blockchains are rewriting the rules of transaction economics in 2025. Gone are the days when a single, static gas fee model dictated user experience and resource allocation. Today, custom app-chains leverage dynamic fee markets to deliver tailored performance, scalability, and cost efficiency for everything from DeFi protocols to gaming ecosystems and enterprise infrastructure.
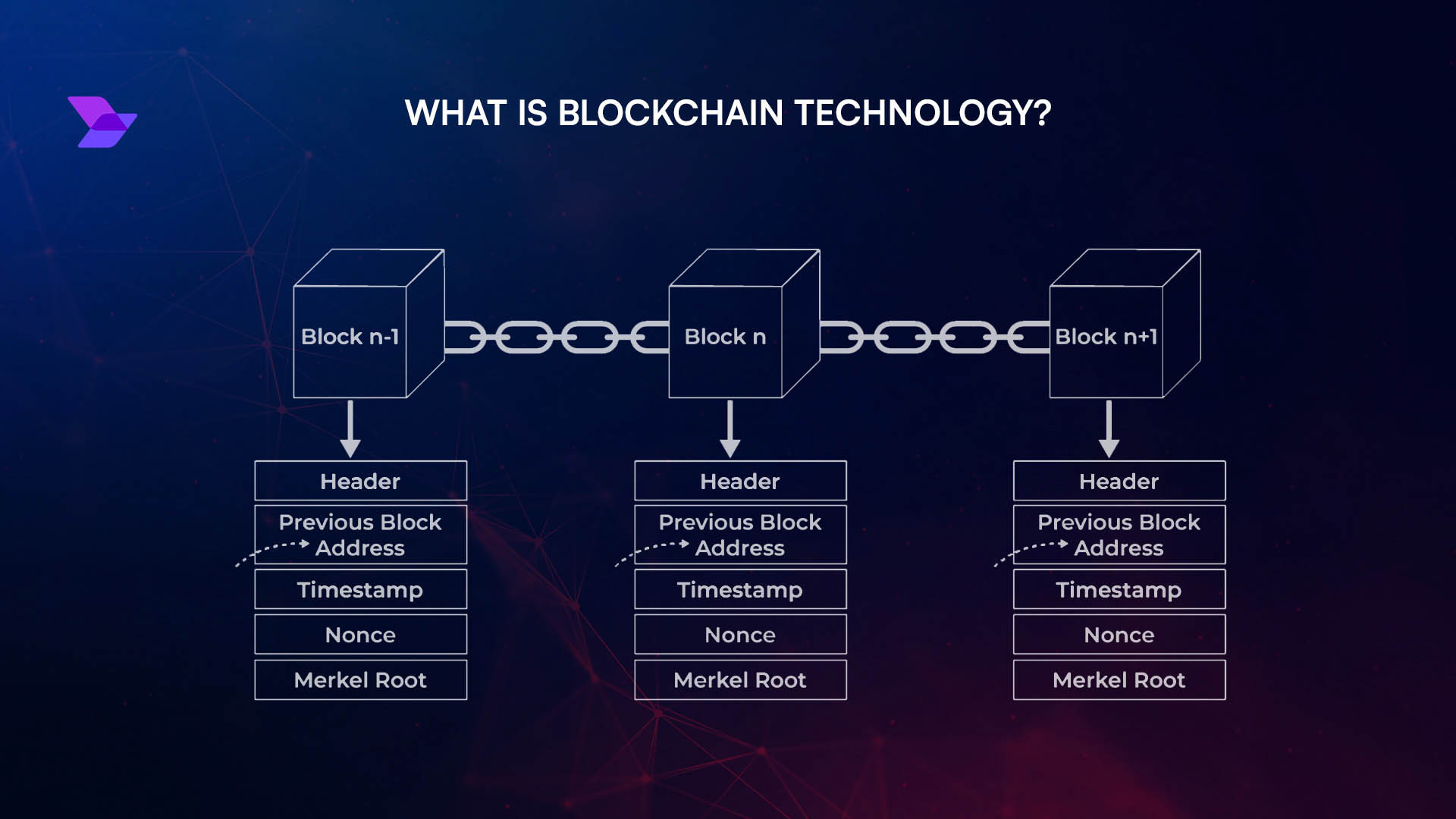
Why Dynamic Fee Markets Are Essential in 2025
The explosion of application-specific blockchains and Layer 3 solutions has created a new landscape where one-size-fits-all pricing simply doesn’t cut it. According to CoinLaw, over 1 million daily active users are now engaging with custom app-chains focused on gaming, DeFi, social, and enterprise use cases. This growth is fueled by demand for low fees, rapid settlement, and specialized functionality that generic Layer 1s can’t match.
Enter dynamic fee markets: flexible pricing engines that respond to real-time network conditions and granular resource usage. Instead of charging users a flat fee per transaction, these systems price computation, storage, bandwidth, and even sequencing priority independently. The result is optimal resource allocation and dramatically improved scalability, two non-negotiables for any serious blockchain project in 2025.
The Mechanics: Multidimensional Pricing and Parallel Execution
Traditional blockchains often use a single metric (like Ethereum’s gas) to price transactions. This approach leads to inefficiencies when different resources are consumed at different rates, think high-compute NFT mints versus simple stablecoin transfers. The new standard is multidimensional fee markets, where each resource gets its own dynamic price tag.
This isn’t just theory, it’s backed by research (arxiv.org) showing that multidimensional designs align incentives between users and validators while minimizing congestion risk. Parallel execution further amplifies throughput but requires sophisticated mechanisms like Gas Computation Mechanisms (GCMs) and Transaction Fee Mechanisms (TFMs) to fairly price concurrent workloads.
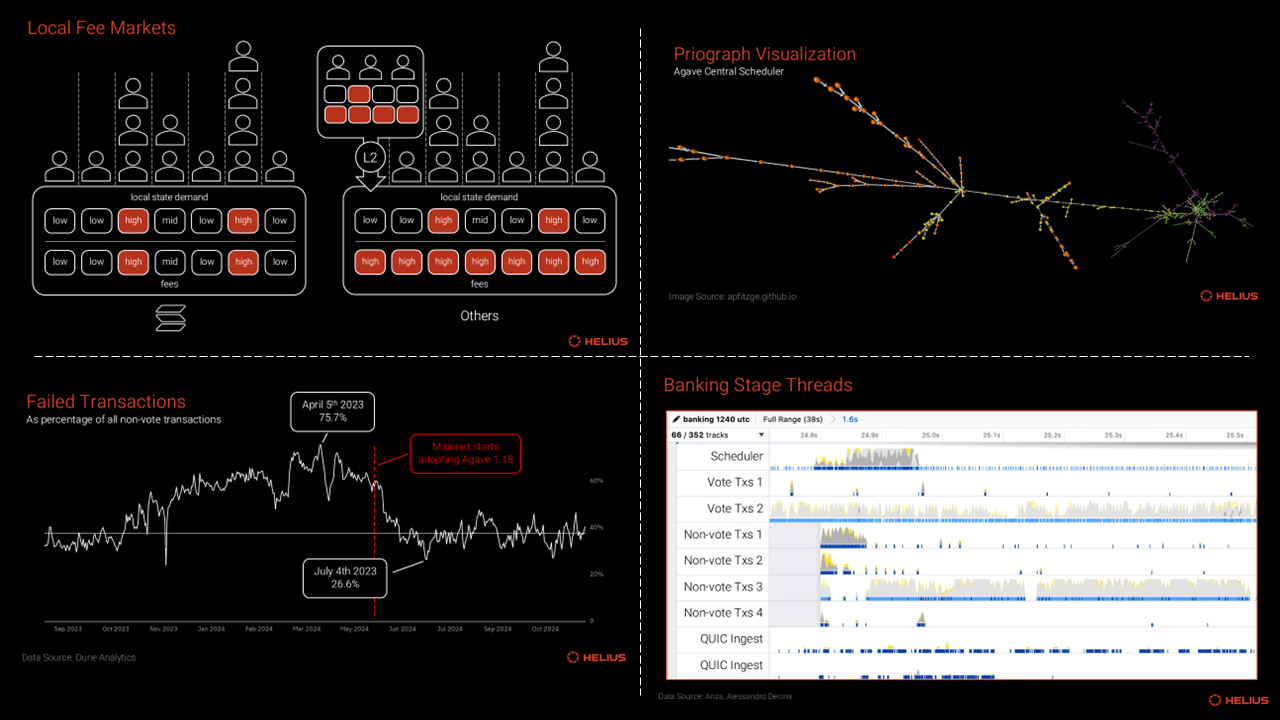
Layer 2 and Beyond: Managing Fees Across the Stack
The rise of Layer 2 (L2) solutions has been a game changer for scalability but brings its own challenges around fee management. Since L2s post batches back to Layer 1s with fluctuating base fees, custom app-chains must implement algorithms that adjust dynamically based on both L1 costs and L2 network congestion (arxiv.org). The interplay between transaction queue dynamics and user response becomes critical, get it wrong, and you risk pricing out your own community or clogging your chain with spam.
This complexity is why many leading projects now adopt unified frameworks that monitor real-time demand across every layer of the stack, ensuring fair access during surges while keeping average transaction costs predictable even as underlying gas prices fluctuate wildly.
Application-Layer Fee Growth: New Revenue Models Emerge
A striking trend in 2025: application-layer fees have started outpacing base protocol fees as dApps build their own micro-economies on top of scalable rollups (finance.yahoo.com). This shift underscores the need for customizable fee structures, letting developers align monetization with actual usage patterns instead of arbitrary network-wide rules.
To capitalize on this shift, forward-thinking teams are deploying maker-taker models, volume-based discounts, and priority queues tailored to their user demographics. For example, high-frequency DeFi traders might be incentivized with lower fees for providing liquidity, while NFT platforms can charge premium rates for instant settlement or storage-heavy operations. The result? A more elastic, demand-driven fee market that maximizes both user satisfaction and protocol revenue.
Top Dynamic Fee Market Patterns for App-Chains (2025)
-
Multidimensional Fee Markets: Price computation, storage, and bandwidth separately to optimize resource allocation and scalability. Example: Ethereum EIP-4844 introduces blob fees for data storage.
-

Dynamic Pricing Mechanisms: Adjust transaction fees in real time based on network demand, deterring congestion and promoting fair access. Example: Ethereum’s EIP-1559 base fee adjustment.
-

Parallel Execution & Fee Structures: Enable parallel transaction processing with tailored fee models for each resource, boosting throughput. Example: Solana’s parallel execution model.
-

Layer 2 Fee Management: Integrate Layer 2 solutions like Arbitrum and Polygon zkEVM to reduce congestion and manage fees efficiently across layers.
-
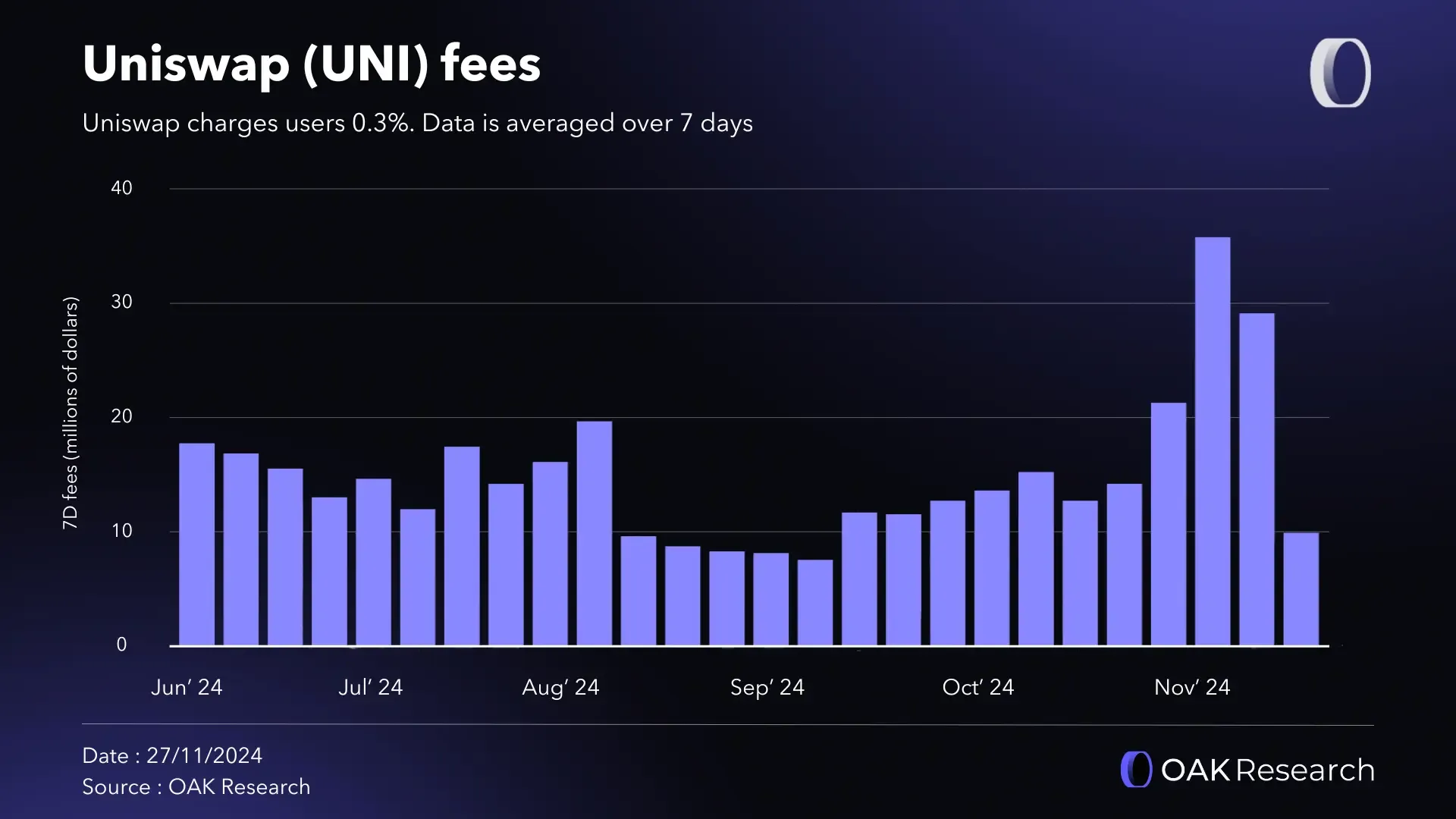
Application-Layer Fee Growth: Design fee markets that prioritize application-specific revenue streams, reflecting the shift toward app-driven on-chain fees. Example: DeFi protocols like Uniswap generating significant fee volume.
-
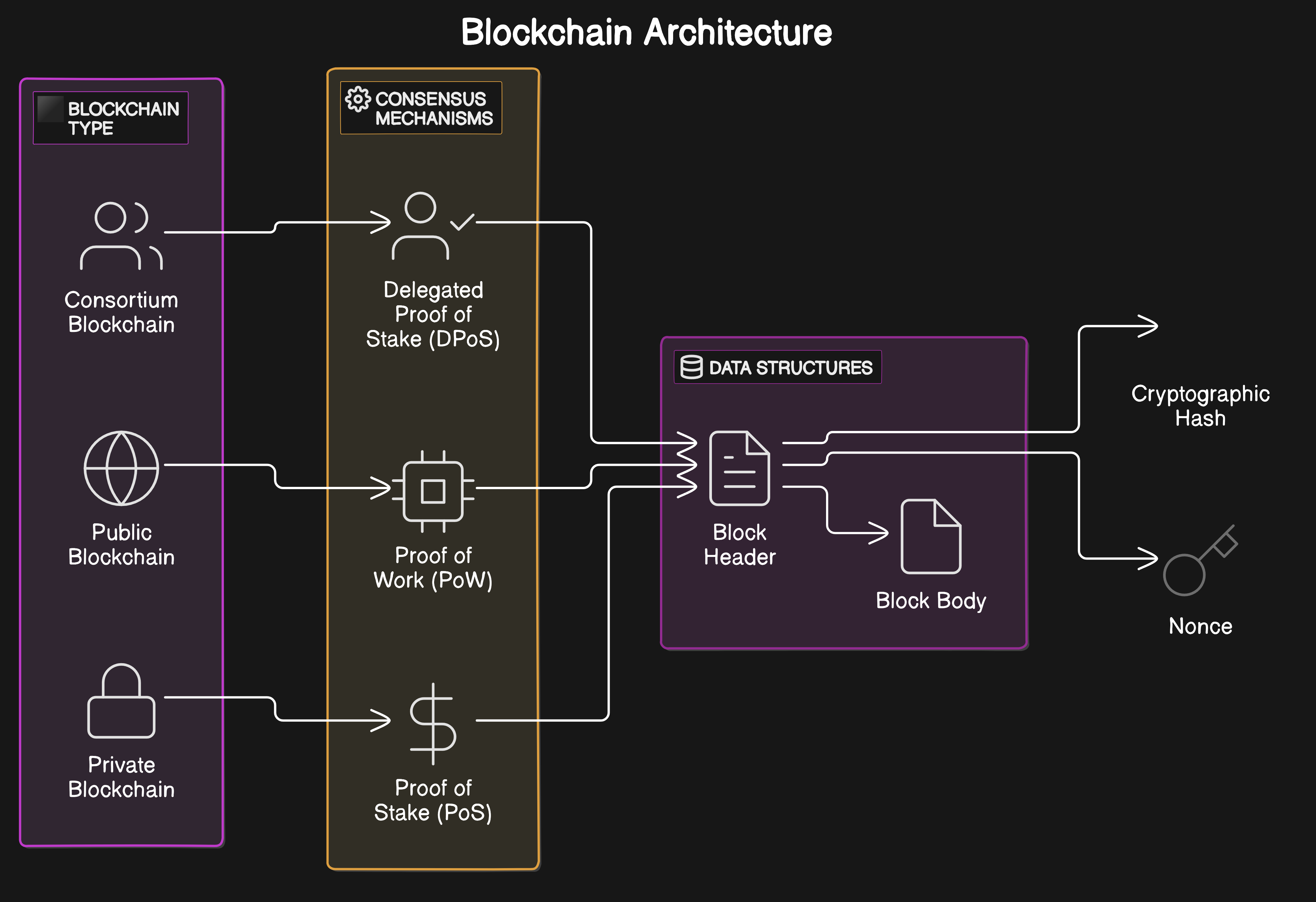
Practical Implementation Considerations: Identify key resources, design adaptive algorithms, align incentives, and ensure security to build robust dynamic fee markets.
But building these advanced markets isn’t just about economics, it’s about engineering. Developers must integrate real-time analytics engines to monitor resource consumption and user behavior. Smart contracts need hooks for dynamic fee recalculation based on network state. And as the number of application-specific blockchains explodes, CoinLaw reports over 1 million daily active addresses on Layer 3s alone, robust monitoring and adaptive algorithms become non-negotiable for maintaining performance at scale.
Best Practices: Building Resilient Custom Fee Markets
Success in 2025’s blockchain landscape requires more than clever pricing formulas. Here are actionable strategies to future-proof your app-chain’s fee market:
- Resource-Aware Metering: Identify which resources (CPU, storage, bandwidth) your dApp stresses most and meter them independently.
- Real-Time Feedback Loops: Use oracles or analytics dashboards to adjust fees dynamically as network demand shifts.
- User-Centric Incentives: Align rewards and discounts with behaviors that benefit the ecosystem, like liquidity provision or batching transactions.
- Security-First Design: Guard against denial-of-service vectors by setting minimum base fees and rate limits that adjust under stress.
If you’re looking for a technical deep-dive into these mechanics, check out our guide on custom fee markets for application-specific blockchains.
The Road Ahead: Unlocking New Blockchain Use Cases
The rise of low-fee blockchains is not just a cost story, it’s unleashing entirely new business models. Social apps can subsidize microtransactions without worrying about L1 spikes. Enterprises can build private rollups with predictable operational costs. Gaming platforms finally offer seamless in-game economies without gas anxiety scaring off players (see real-world examples here).
The bottom line: In 2025, dynamic fee markets are table stakes. They’re the engine behind scalable, sustainable custom app-chains that don’t just survive volatile gas cycles, they thrive on them. Teams that master multidimensional pricing and real-time adjustment will set the pace as blockchain architecture continues its rapid evolution.






