In the evolving landscape of decentralized finance, DeFi lending protocols face mounting pressures from volatile gas fees, front-running risks, and scalability bottlenecks on shared Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks. Custom app-chains with dynamic gas fees emerge as a sophisticated solution, allowing protocols to craft tailored blockchains that prioritize lending-specific transactions while minimizing costs and enhancing efficiency. Platforms like Venus Protocol exemplify this shift, leveraging reduced base gas fees and MEV protections to lock in substantial TVL through atomic borrows resistant to manipulation, particularly for stablecoin-heavy RWAs.

This approach not only stabilizes user experience but also unlocks new economic models. By deploying custom app-chains dynamic gas fees, lending protocols can dynamically adjust costs based on real-time demand, borrower creditworthiness, or even collateral volatility, fostering a more resilient ecosystem.
Challenges Driving the Shift to DeFi Lending Rollups
Traditional Ethereum mainnet and even optimistic rollups struggle under the weight of DeFi lending’s unique demands. High-volume operations like flash loans, collateral liquidations, and interest accruals amplify gas consumption during peak times, leading to unpredictable costs that deter retail users and strain institutional adoption. Recent analyses, including those on EIP-4844’s impact, underscore how Layer 2 rollups can optimize blobs for data availability, yet they fall short for application-specific needs without further customization.
Enter DeFi lending rollups and app-chains: sovereign chains optimized for lending mechanics. Unichain’s model for Uniswap trading hints at broader potential, with revert protections and custom gas policies that could extend to lending by prioritizing supply-demand matching over general-purpose execution. In lending, where precision in oracle updates and liquidation thresholds is paramount, generic infrastructure introduces latency and MEV vulnerabilities. Custom solutions, as seen in Sui’s object-centric fees, enable parallel processing of diverse assets, sidestepping fee market congestion.
DeFi protocols adopting app-chains report up to 90% reductions in effective transaction costs, per insights from Zeeve’s custom blockchain launches for high-performance DeFi.
This migration aligns with vertical integration trends observed by Ark Invest, where protocols control their stack from sequencer to settlement, mirroring SaaS playbooks in fintech.
Mechanics of Dynamic Gas Fees in Specialized Fee Markets
Specialized fee markets DeFi represent the pinnacle of app-chain innovation, where gas auctions evolve beyond EIP-1559’s base-plus-tip model. In a lending-focused app-chain, dynamic fees might tie costs to utilization rates: low during surplus liquidity, surging modestly for urgent liquidations to incentivize keepers without overpenalizing borrowers. This contrasts with static fees, offering predictability while adapting to network load.
Implementation draws from sequencer-level controls in rollups. Developers configure the sequencer to assess transaction priority via metadata, such as loan-to-value ratios or asset volatility scores from integrated oracles. Mathematical models from EIP-4844 studies provide a foundation, modeling gas efficiency as G_opt = min(∑(data_blobs * cost_per_blob), legacy_calldata), but app-chains extend this to fee curves: fee = base and (demand_factor * utilization^γ), where γ tunes sensitivity.
Venus Protocol’s BNB ecosystem illustrates real-world efficacy, with atomic transactions shielding against front-running in stablecoin RWAs post-fee reductions. Such designs not only cut rollup sequencer fees but also democratize access, boosting TVL as users favor chains with intuitive economics.
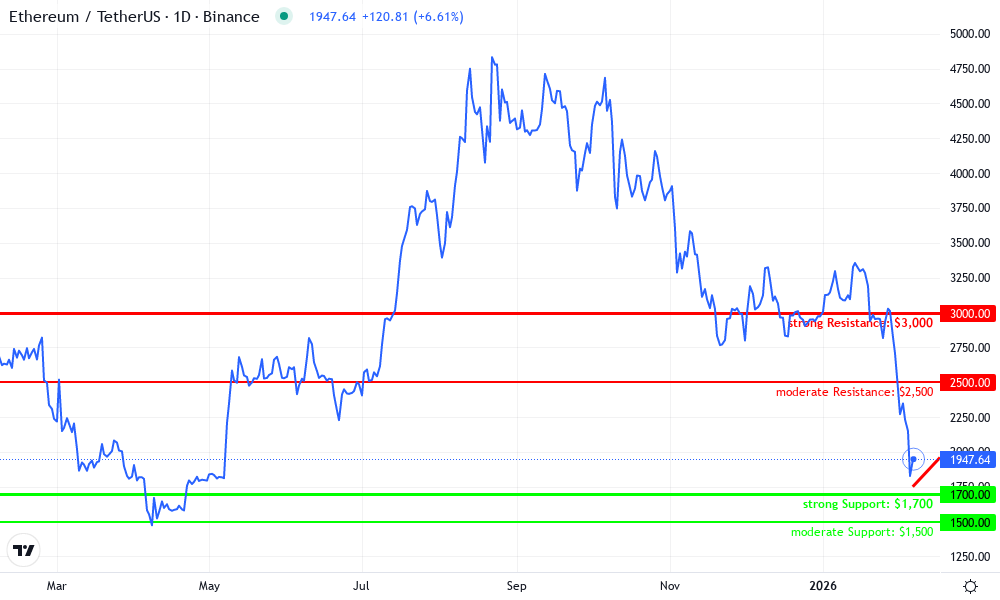
Ethereum Technical Analysis Chart
Analysis by Marlene Hughes | Symbol: BINANCE:ETHUSDT | Interval: 1D | Drawings: 7
Technical Analysis Summary
As Marlene Hughes, my conservative analysis begins with drawing a prominent downtrend line connecting the swing high at approximately 2026-07-15 around $4,800 to the recent low near 2026-02-01 at $1,750, using the ‘trend_line’ tool in red with medium thickness to highlight the dominant bearish channel. Add horizontal lines at key support $1,700 (green, strong) and resistance $2,500 (red, moderate), plus $3,000 (red, strong). Mark the accumulation range from 2026-05-01 to 2026-06-15 with a ‘rectangle’ tool in light blue. Use ‘arrow_mark_down’ at the breakdown from $4,800 peak around 2026-07-20. Place ‘callout’ texts for volume drying up and MACD bearish divergence near recent bars. Fib retracement from low to high for potential pullback levels. Vertical line at 2026-02-06 for current DeFi context review. Keep drawings minimalistic, focusing on high-confidence levels only.
Risk Assessment: high
Analysis: Bearish structure dominates with unconfirmed reversal signals; macro DeFi positives not yet priced in amid volatility.
Marlene Hughes’s Recommendation: Remain sidelined, allocate to fixed income; monitor for $1,700 support hold before considering small positions.
Key Support & Resistance Levels
📈 Support Levels:
-
$1,700 – Recent lows holding as psychological support tied to 2026 DeFi fee reductions.
strong -
$1,500 – Deeper macro support if breakdown occurs.
moderate
📉 Resistance Levels:
-
$2,500 – Initial resistance from prior consolidation highs.
moderate -
$3,000 – Major resistance from mid-2026 downleg pivot.
strong
Trading Zones (low risk tolerance)
🎯 Entry Zones:
-
$2,400 – Short entry on rejection at resistance with tight stop, aligning low risk tolerance.
medium risk -
$1,650 – Long only on confirmed support hold with volume spike, but prefer wait.
high risk
🚪 Exit Zones:
-
$3,000 – Profit target for shorts if uptrend resumes.
💰 profit target -
$1,600 – Stop loss below key support for any longs.
🛡️ stop loss
Technical Indicators Analysis
📊 Volume Analysis:
Pattern: declining on downmove
Volume drying up suggests weakening seller conviction, potential base forming but unconfirmed.
📈 MACD Analysis:
Signal: bearish divergence
MACD histogram contracting while price tests lows, hinting exhaustion.
Applied TradingView Drawing Utilities
This chart analysis utilizes the following professional drawing tools:
Disclaimer: This technical analysis by Marlene Hughes is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as financial advice.
Trading involves risk, and you should always do your own research before making investment decisions.
Past performance does not guarantee future results. The analysis reflects the author’s personal methodology and risk tolerance (low).
Designing App-Chain Fee Optimization for Lending Efficiency
App-chain fee optimization begins with sequencer customization. Unlike shared L2s, app-chains grant full sovereignty over fee markets, enabling hooks akin to Uniswap’s for dynamic experimentation. For lending, integrate MEV auctions where searchers bid for liquidation rights, channeling extracted value back to the protocol treasury rather than external bots.
Consider a protocol handling RWAs: fees scale with asset risk profiles, computed via on-chain risk engines. This thoughtful calibration, informed by MixBytes’ modern lending implementations, ensures high-throughput without compromising decentralization. Early adopters like those in Robinhood’s rollup lineage demonstrate custom L2s’ edge in user protections, paving the way for lending apps to embed revert-on-failure for overcollateralized positions.
Read more on how dynamic fee markets power scalable custom app-chains for deeper technical dives.
To translate these concepts into reality, developers must navigate the sequencer configuration and smart contract integrations with precision. This is where rollup sequencer fees become a strategic lever, allowing protocols to subsidize low-risk deposits while charging premiums for high-leverage positions, all calibrated through on-chain governance.
Sequencer Launch Script: Dynamic Fees & MEV Integration
To launch a custom app-chain tailored for DeFi lending protocols, we need to configure the sequencer with dynamic gas fees to handle fluctuating demand from deposits, loans, and liquidations. This prevents fee spikes while ensuring liveness. MEV integration further optimizes by allowing searchers to bid for transaction ordering, capturing value from arbitrage in lending markets. The following bash script sets this up using Docker for reproducibility—thoughtfully parameterized for easy tuning.
#!/bin/bash
set -e
# Educational note: This script launches a sequencer for a custom DeFi lending app-chain.
# It incorporates dynamic gas fees via environment variables (EIP-1559 style)
# and MEV integration for optimizing transaction ordering in lending/borrowing ops.
echo "🚀 Launching DeFi Lending App-Chain Sequencer with Dynamic Gas Fees & MEV..."
# Prerequisites: Ensure Docker and Docker Compose are installed.
# Assumes a docker-compose.yml with services like PostgreSQL (for lending state)
# and Redis (for mempool buffering).
# Start dependencies
docker-compose up -d db mempool
# Dynamic Fee Curve Parameters
# These define the fee adjustment logic:
# - BASE_FEE: Initial base fee in wei (1 gwei)
# - TARGET_GAS: Target gas per block (15M typical for app-chains)
# - MAX_FEE: Cap to prevent fee explosions
export BASE_FEE=1000000000
export TARGET_GAS=15000000
export MAX_FEE=50000000000 # 50 gwei
# MEV Integration: Enable flashbots-style auctions for profitable reordering
# Optimizes gas costs by prioritizing high-value DeFi txs (e.g., liquidations)
export MEV_ENABLED=true
export MEV_BUILDER_URL="http://mev-boost:18550"
# Launch the sequencer container
# In a real setup, use your app-chain image (e.g., based on OP Stack or Cosmos SDK)
docker run -d \
--name defi-lending-sequencer \
--network appchain-net \
-p 8545:8545 \
-p 8546:8546 \
-e "DYNAMIC_FEES=true" \
-e "BASE_FEE=$BASE_FEE" \
-e "TARGET_GAS=$TARGET_GAS" \
-e "MAX_FEE=$MAX_FEE" \
-e "MEV_ENABLED=$MEV_ENABLED" \
-e "MEV_BUILDER_URL=$MEV_BUILDER_URL" \
op-stack/sequencer:latest # Replace with your custom image
# Health check
echo "✅ Sequencer logs:"
docker logs defi-lending-sequencer --tail 10
echo "
📊 Monitor: docker logs -f defi-lending-sequencer"
echo "🔗 RPC Endpoint: http://localhost:8545"
echo "💡 Tip: The sequencer will adjust base_fee = max(0, base_fee + (gas_used - target_gas) * elasticity), where elasticity ~0.125, per block."Run this script in your project root (with docker-compose.yml for deps). In production, secure endpoints, use Kubernetes for scaling, and audit the fee curve for your protocol’s economics. This setup ensures cost-efficient sequencing: low fees during idle periods, adaptive rises under load, and MEV revenue sharing to subsidize users. Experiment with TARGET_GAS based on your lending tx sizes! Next, deploy your smart contracts to this chain.
Following this blueprint, protocols can achieve sovereignty over their fee markets. A core element involves coding the dynamic fee logic directly into the app-chain’s execution layer. Here’s a simplified Solidity snippet demonstrating a utilization-based fee adjustment for lending transactions:
Solidity Implementation: Dynamic Gas Fee Calculation Using Utilization and Oracle Data
In a custom app-chain for DeFi lending protocols, dynamically adjusting gas fees based on pool utilization and oracle data helps maintain network stability and incentivizes balanced usage. High utilization rates signal congestion risk, warranting higher fees, while oracle data (e.g., ETH price) can account for market volatility. The following Solidity contract snippet illustrates a `calculateDynamicGasMultiplier` function that computes a fee adjustment multiplier. This could be invoked by your chain’s sequencer or validator to scale the base fee in real-time.
```solidity
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
interface IOracle {
function getLatestPrice() external view returns (uint256);
}
contract DeFiLendingPool {
uint256 public constant PRECISION = 1e18;
uint256 public totalSupply;
uint256 public totalBorrow;
IOracle public priceOracle;
constructor(address _oracle) {
priceOracle = IOracle(_oracle);
}
function updateTotals(uint256 _totalSupply, uint256 _totalBorrow) external {
totalSupply = _totalSupply;
totalBorrow = _totalBorrow;
}
function getUtilizationRate() public view returns (uint256) {
if (totalSupply == 0) return 0;
return (totalBorrow * PRECISION) / totalSupply;
}
function calculateDynamicGasMultiplier(uint256 baseGasFee) public view returns (uint256) {
uint256 utilization = getUtilizationRate();
uint256 ethPrice = priceOracle.getLatestPrice(); // ETH/USD price with 18 decimals
// Utilization-based multiplier
uint256 utilMultiplier;
if (utilization >= 0.95 * PRECISION) {
utilMultiplier = 3 * PRECISION;
} else if (utilization >= 0.90 * PRECISION) {
utilMultiplier = 2 * PRECISION;
} else if (utilization >= 0.80 * PRECISION) {
utilMultiplier = 1.5 * PRECISION;
} else {
utilMultiplier = PRECISION;
}
// Price-based multiplier (high ETH price indicates potential volatility)
uint256 priceMultiplier = ethPrice > 2500 * 1e18 ? 1.2 * PRECISION : PRECISION;
// Combined multiplier applied to base fee
return (baseGasFee * utilMultiplier * priceMultiplier) / (PRECISION * PRECISION);
}
}
```This example uses a tiered utilization model and a simple price threshold for illustration. In practice, integrate robust oracles like Chainlink, add governance for parameter updates, and ensure the function is gas-efficient for frequent calls. The resulting dynamic fee promotes sustainable usage patterns in your lending app-chain, preventing over-utilization during volatile market conditions.
This code exemplifies how to hook into the sequencer’s fee oracle, pulling real-time utilization from lending pools to modulate base fees. In practice, deploy this on frameworks like OP Stack or Cosmos SDK, customized for lending primitives. Venus Protocol’s success stems from similar mechanics, where atomic BNB borrows post-fee reductions have fortified stablecoin RWAs against front-running, sustaining high TVL amid market volatility.
From a fundamentals-first perspective, these optimizations mirror traditional fixed-income strategies, where yield curves adjust to credit risk. DeFi lending app-chains extend this logic on-chain, with dynamic fees acting as a yield-adjusting mechanism that rewards liquidity providers during stress periods without eroding borrower incentives.
Custom app-chains enable parallel asset processing akin to Sui’s model, decoupling fee interactions and boosting throughput for diverse lending portfolios.
Yet, challenges persist. Governance over fee parameters demands robust tokenomics to prevent capture by whales, while interoperability with Ethereum settlement layers requires careful bridging designs. Insights from Wharton’s DeFi-TradFi analysis highlight how institutional adoption hinges on such reliability, positioning app-chains as bridges between decentralized innovation and regulated finance.
Measuring Success: Metrics for App-Chain Fee Optimization
Evaluate app-chain fee optimization through key performance indicators: effective gas cost per transaction, MEV recapture rates, and TVL growth adjusted for volatility. Protocols like those in the Hook ecosystem experiment with custom AMMs under dynamic fees, yielding insights transferable to lending. For instance, a lending app-chain might target sub-cent fees during normal operations, scaling to pennies for liquidations, as modeled in EIP-4844 gas analyses.
Real-world benchmarks from Zeeve’s DeFi deployments show custom blockchains slashing costs by orders of magnitude compared to optimistic rollups, where shared sequencer queues introduce delays. Robinhood’s rollup experiments further validate tailored gas policies, with revert protections shielding users from sandwich attacks prevalent in generic L2s.
Explore further in our guide on custom app-chains specialized fee markets for DeFi cost optimization 2025.
Looking ahead, the convergence of RWAs and dynamic fees heralds a new era for DeFi lending. As protocols verticalize their stacks, following Ark Invest’s SaaS playbook, app-chains will not merely scale transactions but redefine economic fairness. Lenders gain predictable costs, borrowers access efficient capital, and the ecosystem thrives on captured value recirculated via treasuries. This thoughtful evolution, grounded in proven mechanics, positions custom app-chains as the infrastructure cornerstone for sustainable DeFi growth.