Building custom fee markets for application-specific rollups is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of blockchain scalability and economic alignment. As the modular blockchain landscape matures, developers are moving beyond generic transaction fees to deploy specialized fee structures that optimize for their unique dApp requirements. The strategies outlined here reflect the latest research and best practices in the field, enabling teams to unlock new levels of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and user engagement.

Why Custom Fee Markets Matter for App-Chains
Generic fee models can hinder both performance and adoption. Application-specific rollups allow developers to tailor every aspect of their chain, including how fees are collected, distributed, and priced. This flexibility is crucial for scaling high-throughput dApps, supporting microtransactions, or incentivizing specialized actors like ZK provers. By designing bespoke fee markets, projects can:
- Reduce transaction costs for end-users
- Dynamically allocate resources based on real-time demand
- Create sustainable incentives for validators and infrastructure providers
- Align token economics with long-term growth strategies
The following five strategies represent the cutting edge of custom fee market design for application-specific rollups.
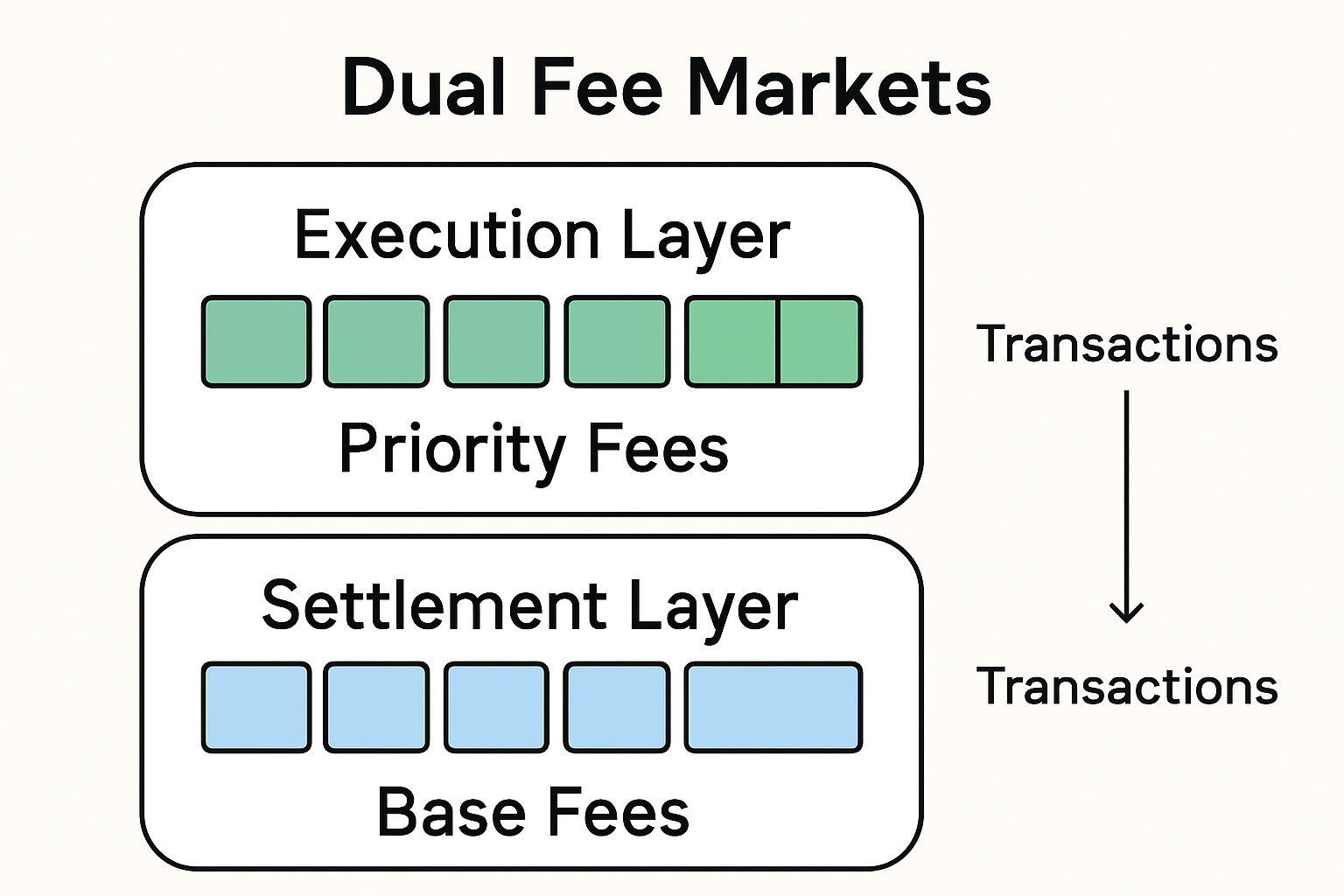
1. Implement Dual Fee Markets: Decoupling Data Availability and Execution Costs
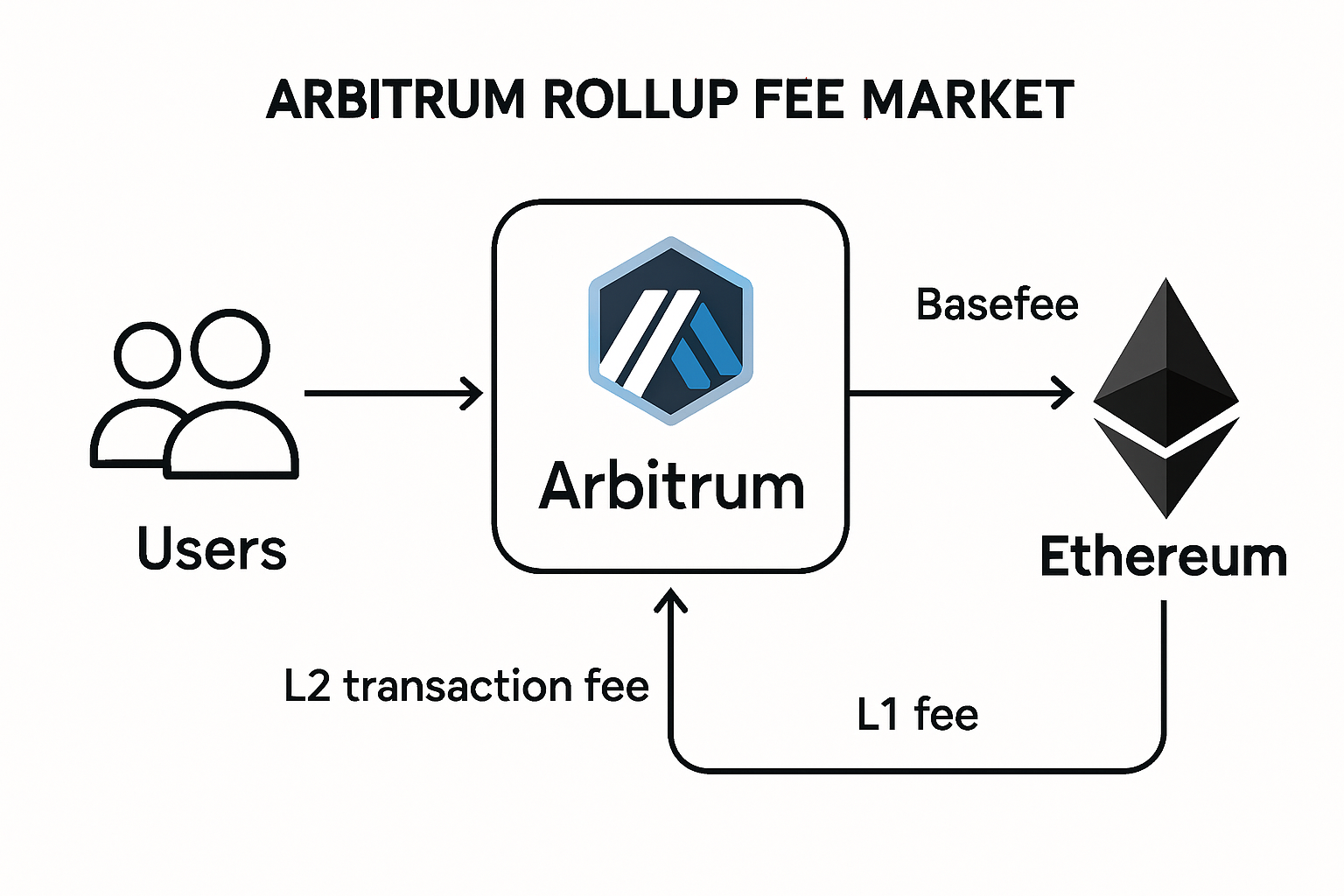
A defining feature of modern rollup architectures is their ability to separate base layer data availability fees from rollup execution fees. This dual-market model allows pricing to be optimized independently for each resource:
- Base layer fees: Cover the cost of posting transaction data to Ethereum or another parent chain, directly impacting security and censorship resistance.
- Execution fees: Reflect computation performed within the rollup’s virtual machine or state transition function.
This separation enables dynamic pricing based on distinct demand curves, crucial for balancing security guarantees with affordable execution. Teams deploying custom rollups via Rollups-as-a-Service platforms can configure these parameters from day one (see Alchemy’s guide on RaaS deployment). As highlighted in recent research (DROPS report on multidimensional fee markets), dual fee markets are now standard practice among leading app-chains.
2. Adopt Usage-Based Fee Models: Fair Pricing That Rewards Efficiency
The next frontier is usage-based pricing models, where users pay according to actual computational or storage resources consumed within the rollup. Unlike flat gas models inherited from L1 chains, this approach:
- Makes costs predictable and transparent for users with varying needs.
- Punishes inefficient smart contract design while rewarding optimization.
- Lowers barriers for applications that require high throughput but low per-transaction cost (e. g. , gaming, DeFi microtrades).
This granular accounting is especially valuable when paired with multi-dimensional resource tracking, measuring not just compute cycles but also storage footprint and bandwidth utilization (Solana Compass resource on multi-dimensional fee markets). The result: a more equitable system that drives innovation across diverse dApp verticals.
5 Actionable Strategies for Custom Fee Markets in Rollups
-
Adopt Usage-Based Fee Models: Design fee structures that charge users based on actual computational or storage resources consumed within the rollup. This approach, inspired by Ethereum’s gas model and Solana’s multi-dimensional fees, ensures fair pricing and incentivizes efficient dApp design.
-
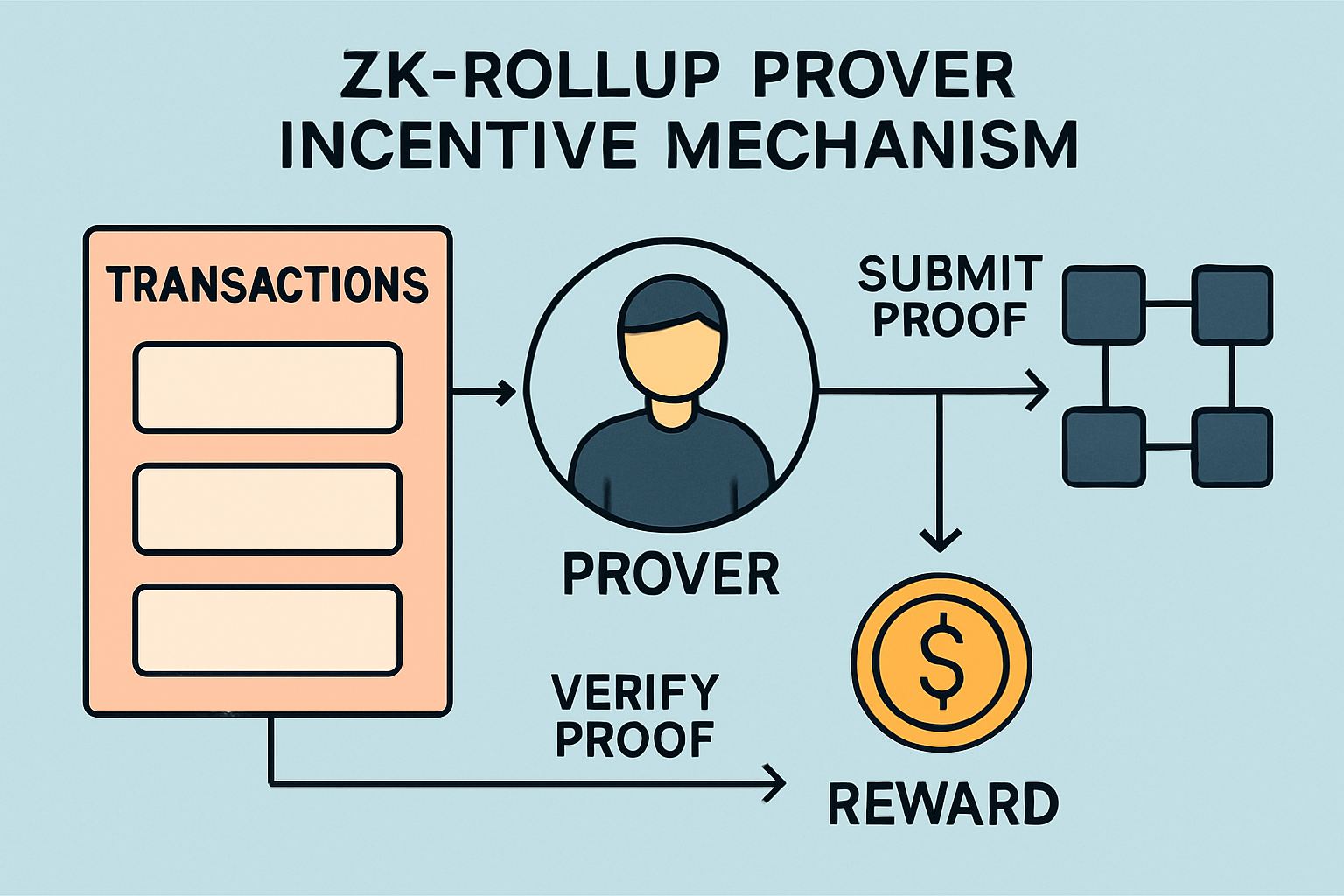
Integrate Prover Incentive Mechanisms: Establish sustainable fee markets for ZK- or optimistic rollup provers, ensuring prover costs are covered and reliable proof generation is incentivized. Platforms like Polygon zkEVM and Scroll exemplify this approach.
-
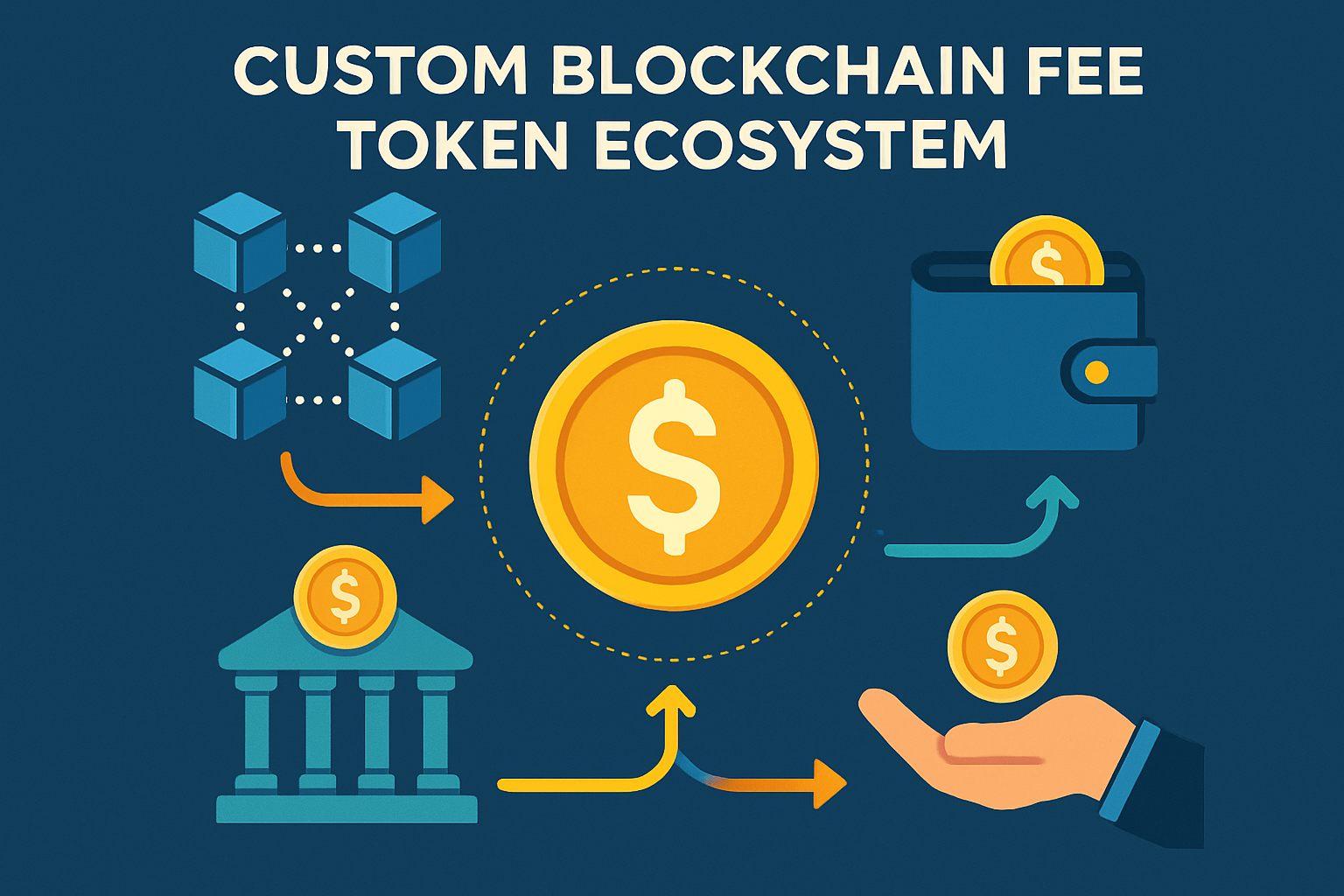
Enable Customizable Fee Tokens: Allow applications to accept and distribute fees in their native app tokens, supporting new cash flow models and aligning incentives between users, developers, and validators. Solutions such as Arbitrum Orbit and Cartesi Rollups enable this flexibility.
-
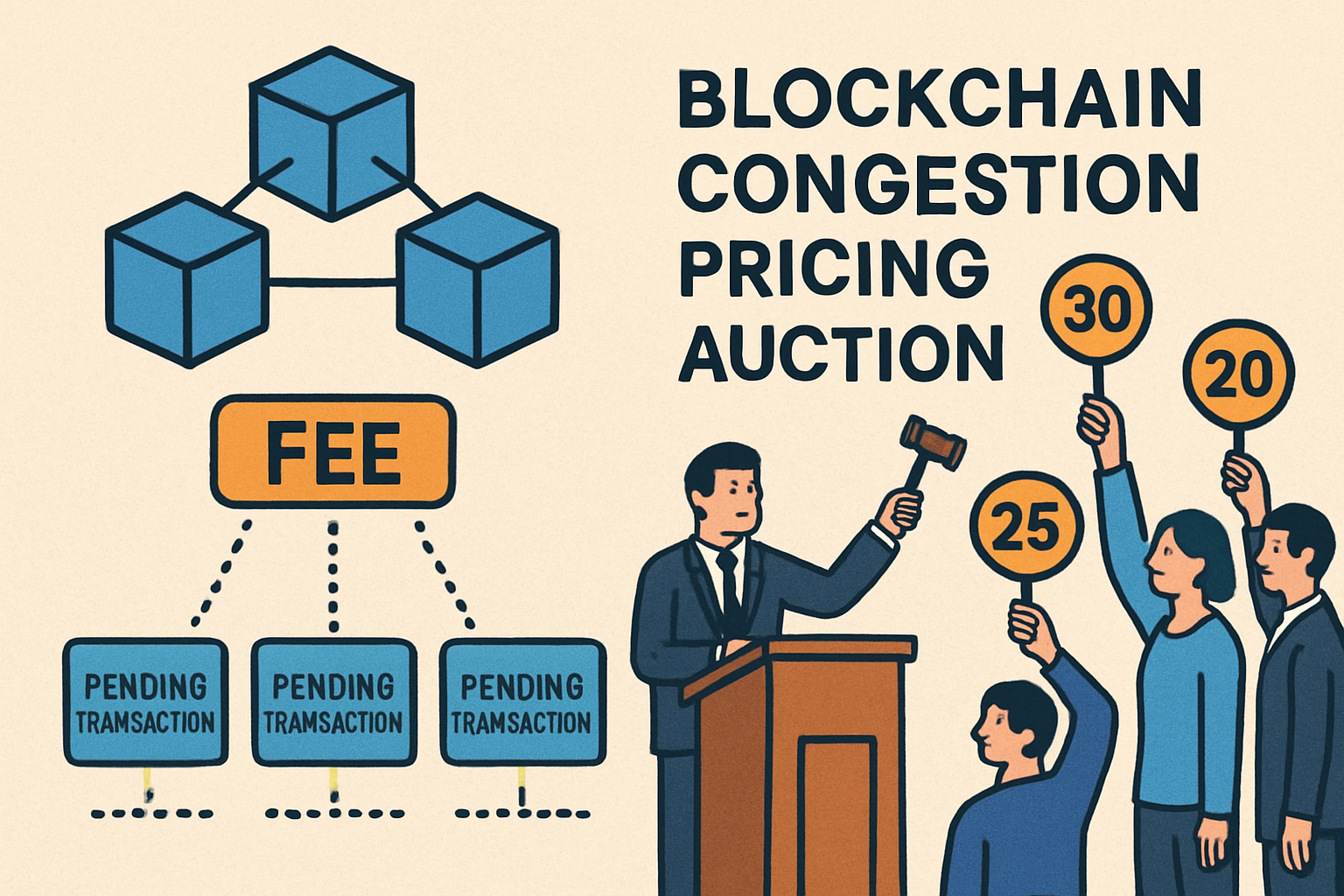
Utilize Congestion Pricing and Priority Queues: Introduce flexible fee tiers or auction-based systems during high demand to allocate limited rollup resources efficiently and maintain low latency for critical transactions. EIP-1559 and Sui’s priority gas auctions are leading examples.
3. Integrate Prover Incentive Mechanisms: Sustainable Proof Generation at Scale
No discussion of application-specific rollup economics is complete without addressing prover incentives, especially as ZK-rollups gain traction. In these systems, provers generate cryptographic proofs attesting to state transitions; their costs must be covered by user fees to maintain network liveness and security.
The most robust designs establish sustainable prover incentive mechanisms through competitive bidding or staking frameworks (arXiv: Mechanism Design for ZK-Rollup Prover Markets). By allowing provers to compete on price or stake collateral against proof validity, chains can ensure:
- Sufficient compensation for prover hardware and operational expenses;
- An open market that encourages efficiency improvements;
- A healthy balance between user affordability and prover profitability.
As ZK and optimistic rollups continue to scale, the complexity of proof generation grows. Without carefully designed incentive mechanisms, provers may be underpaid, risking network congestion or delayed finality. By integrating competitive fee markets, where provers bid for the right to generate proofs or stake tokens as a security guarantee, application-specific rollups can maintain reliable throughput and minimize downtime. This is a critical factor for dApps that require rapid settlement and uninterrupted service.
4. Enable Customizable Fee Tokens: Aligning Economic Incentives with App Ecosystems
The ability to accept and distribute fees in native application tokens is transforming app-chain economics. Instead of relying solely on Ethereum’s ETH or another base token, custom rollups can support their own gas tokens or even multiple fee currencies. This flexibility not only improves user experience but also enables new business models:
- Direct cash flows to token holders, validators, or developers via protocol-level fee distribution (a16z crypto: Cash flows for app tokens).
- Flexible compliance options for regulated environments by supporting whitelisted tokens.
- Stronger alignment between network usage and token value accrual, driving long-term ecosystem growth.
This approach is especially relevant for DeFi platforms, gaming ecosystems, and creator economies looking to build sustainable revenue streams within their own communities. By leveraging customizable fee tokens, projects can unlock novel incentive structures that were previously unattainable on monolithic L1s.
5. Utilize Congestion Pricing and Priority Queues: Efficient Resource Allocation During Peak Demand
Even with advanced scalability solutions, resource contention during periods of high demand remains a challenge. Application-specific rollups are now adopting congestion pricing models, such as flexible fee tiers or auction-based systems, to allocate limited blockspace efficiently:
- Priority queues: Users willing to pay higher fees can ensure their transactions are processed first, maintaining low latency for mission-critical operations.
- Auction-based block inclusion: Dynamic auctions allow users to compete for space in each block when demand spikes.
- Smooth user experience: By making pricing transparent and responsive to real-time conditions, chains avoid persistent congestion and sudden fee spikes.
This technique not only maximizes throughput but also generates additional protocol revenue during peak times, a win-win for both users needing urgent settlement and validators seeking higher returns.
The Road Ahead: Continuous Optimization in Custom Fee Markets
The landscape of custom fee markets is evolving rapidly alongside advances in rollup frameworks and modular blockchain infrastructure. As more teams deploy application-specific rollups using RaaS providers (Alchemy’s RaaS overview), the ability to iterate on fee market design will become a key differentiator in user experience and economic sustainability.
The strategies outlined above, dual fee markets, usage-based pricing, prover incentives, custom fee tokens, and congestion pricing, are not mutually exclusive. The most successful app-chains will combine these mechanisms into cohesive systems tailored to their unique requirements. Ongoing monitoring with robust analytics tools will be essential; as network conditions evolve, so too must the underlying economics.
5 Actionable Strategies for Custom Fee Markets in Rollups
-

Integrate Prover Incentive Mechanisms: Establish sustainable fee markets for ZK- or optimistic rollup provers, ensuring that prover costs are covered and incentivizing reliable proof generation through competitive bidding or staking. Polygon zkEVM and Scroll exemplify this with their active prover markets.
-

Enable Customizable Fee Tokens: Allow applications to accept and distribute fees in their native app tokens, supporting new cash flow models and aligning economic incentives between users, developers, and validators. Arbitrum Orbit and OP Stack enable custom gas tokens for rollups.
-
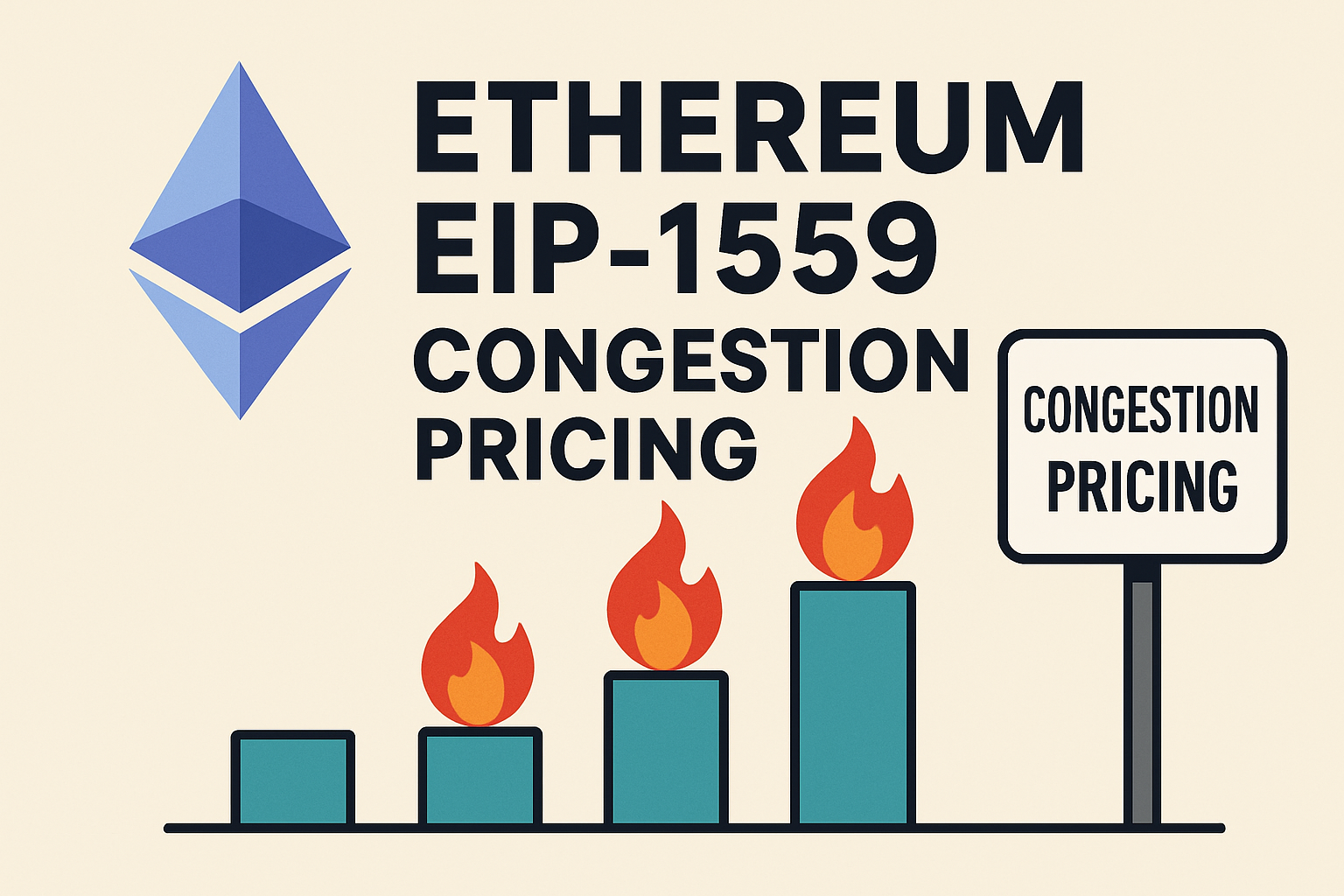
Utilize Congestion Pricing and Priority Queues: Introduce flexible fee tiers or auction-based systems during periods of high demand to allocate limited rollup resources efficiently and maintain low latency for critical transactions. EIP-1559 inspired models and Base implement dynamic fee adjustments to manage congestion.